![]() When
editing a layer in ArcMap, make sure you use the Save Edits option on the Editor
toolbar to save edits as a separate process from saving your map.
When
editing a layer in ArcMap, make sure you use the Save Edits option on the Editor
toolbar to save edits as a separate process from saving your map.
Command: BUFFER
Commands: APPEND, CLIP, ERASE, MAPJOIN, SPLIT, UPDATE
Commands: DISSOLVE, ELIMINATE, RESELECT
Commands: IDENTITY, INTERSECT, UNION
In this exercise we will concentrate on the SPATIAL JOIN commands.
Criteria A ) Locate all areas which have either ponderosa pine vegetation or are owned by the National Forest Service. Coverages = (1) NATVEG = (2) LNDOWNER Items (values) = (1) DESCRIP ('*PONDEROSA*') = (2) LANDOWNER ('NFS') Criteria B ) Locate all areas that belong to the Forest Service and all areas containing ponderosa pine within this forest service land. Coverages = (1) NATVEG = (2) LNDOWNER Items (values) = (1) DESCRIP ("*PONDEROSA*") = (2) LANDOWNER ("NFS") Criteria C ) Locate all areas which have both ponderosa pine and belong to the forest service. Coverages = (1) NATVEG = (2) LNDOWNER Items (values) = (1) DESCRIP ("*PONDEROSA*") = (2) LANDOWNER ("NFS")
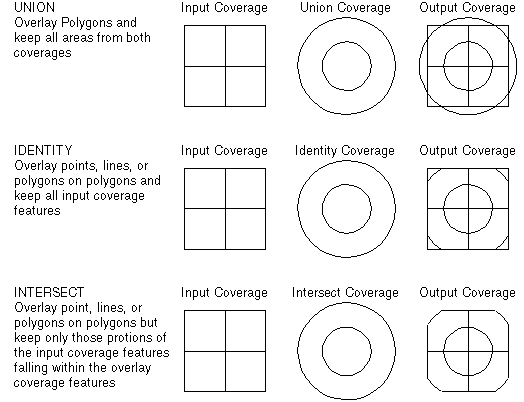
Figure 1. Diagram illustrating the use of three
polygon overlay commands:
UNION, INTERSECT, and IDENTITY.
Step 2: Copy the lndowner and natveg coverages from flag24/cover to your Z:\ workspace.
Step 3: Preview the geography and tables of both coverages to familiarize yourself with them.
Step 4: Combine features of the input coverage (lndowner) with features of the overlay coverage (vegetation) so that the resulting coverage contains what is given in Criteria A.
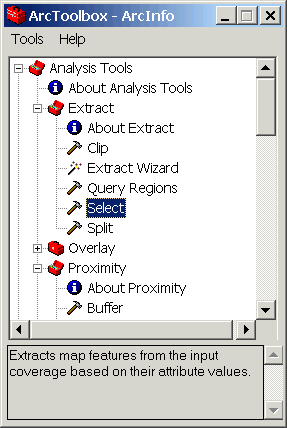
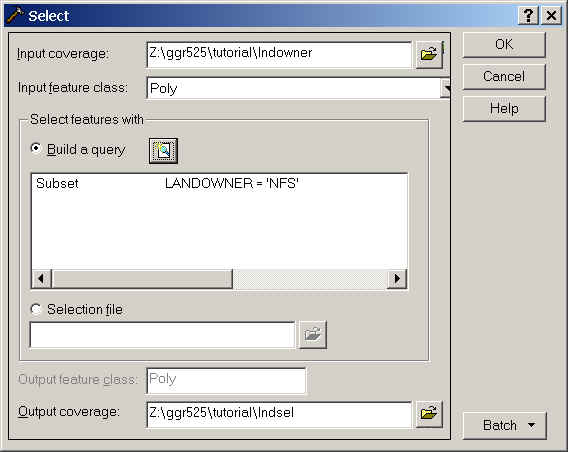
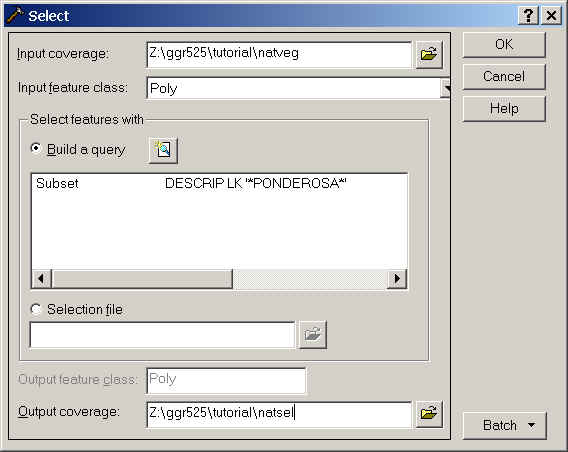
From ArcToolbox, choose Overlay/Union.
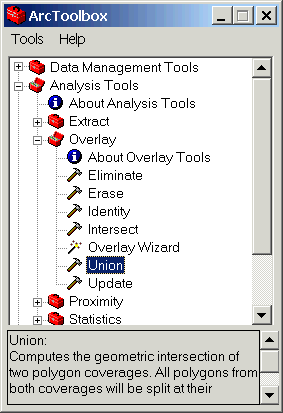
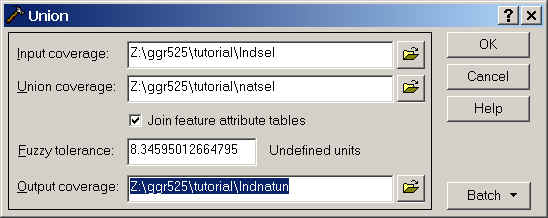
The input coverage is lndsel, the union coverage is natsel
and name the output lndnatun. You will want attributes from both
tables so be sure that Join feature attribute tables is
checked.
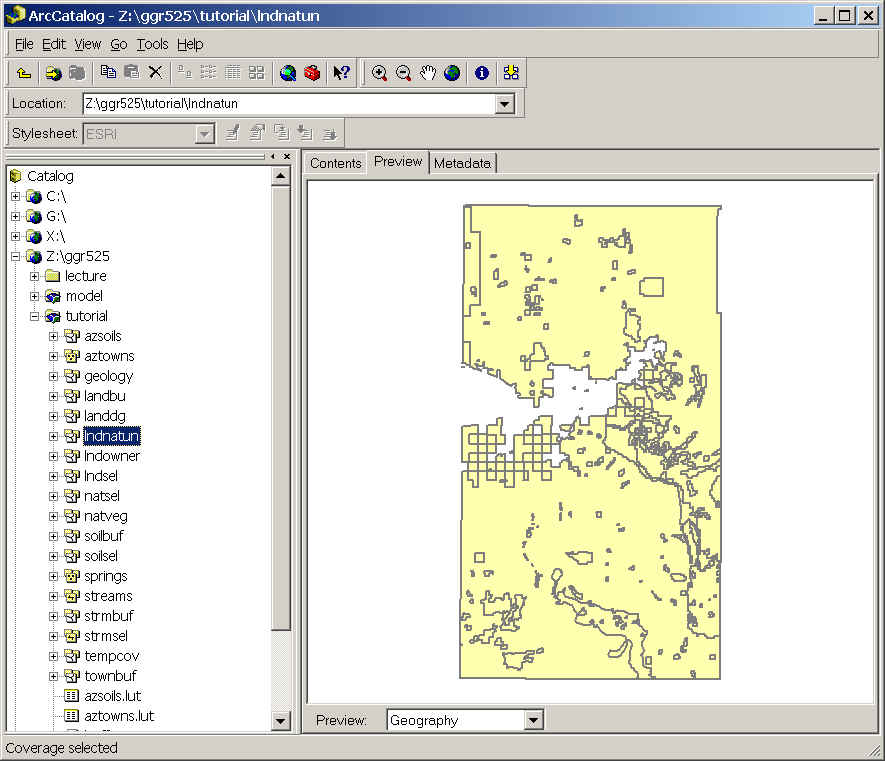
Preview the geography of the output in ArcCatalog noticing
where vegetation features have been added to ownership features.
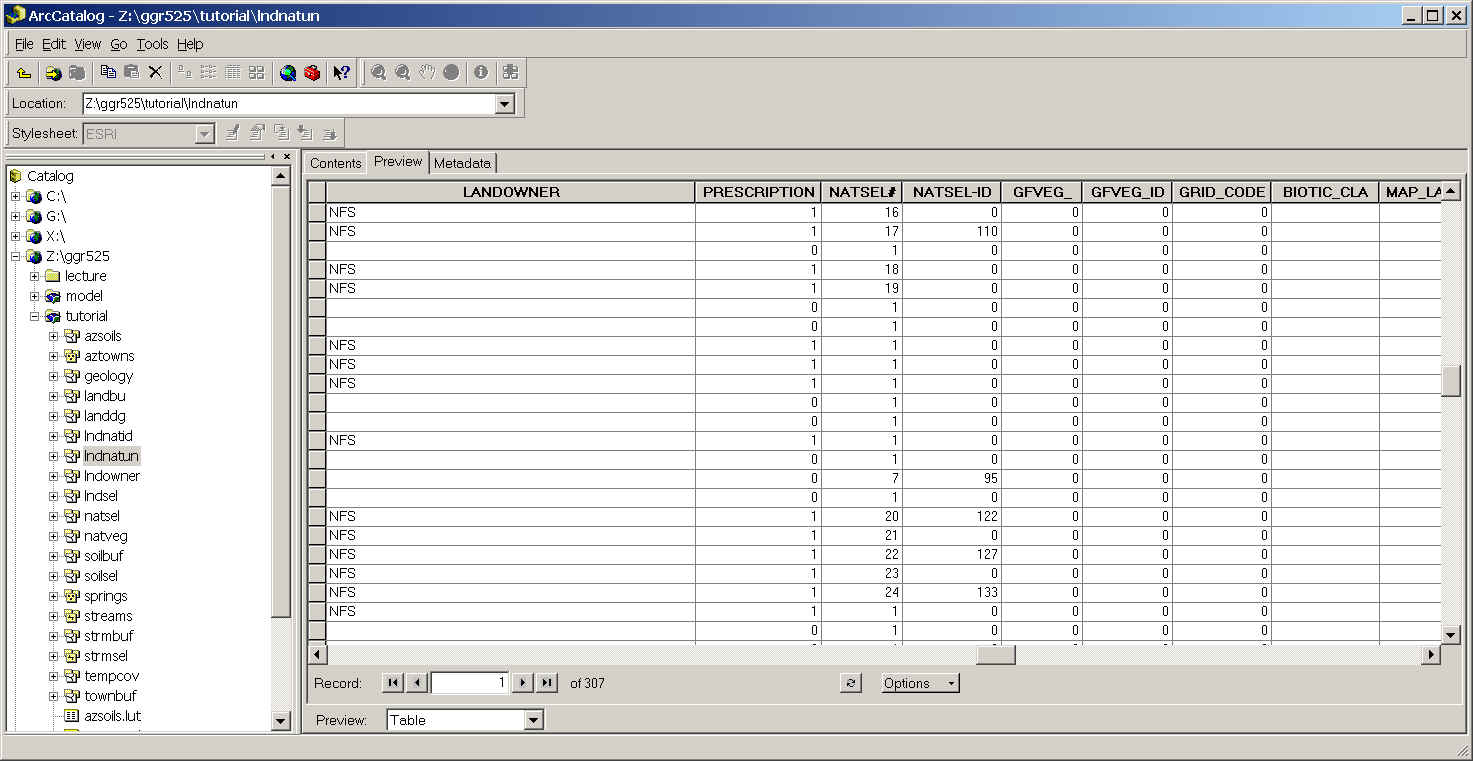
Preview the table and notice how attributes from both coverages exist
in the table now.
Step 6: Now combine features of the input coverage (lndsel) with the features of the overlay coverage (natsel) so that the output coverage meets requirements in Step 1 Criteria B.

Step 7: Combine the features of the input coverage (lndsel) with the features of the overlay coverage (natsel) so that the output coverage meets the requirements of Step 1 Criteria C.
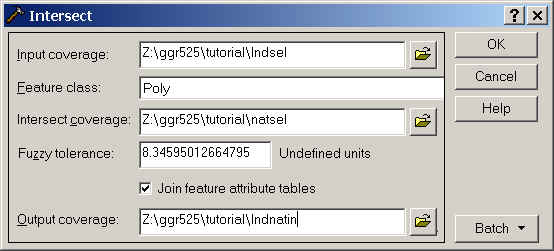
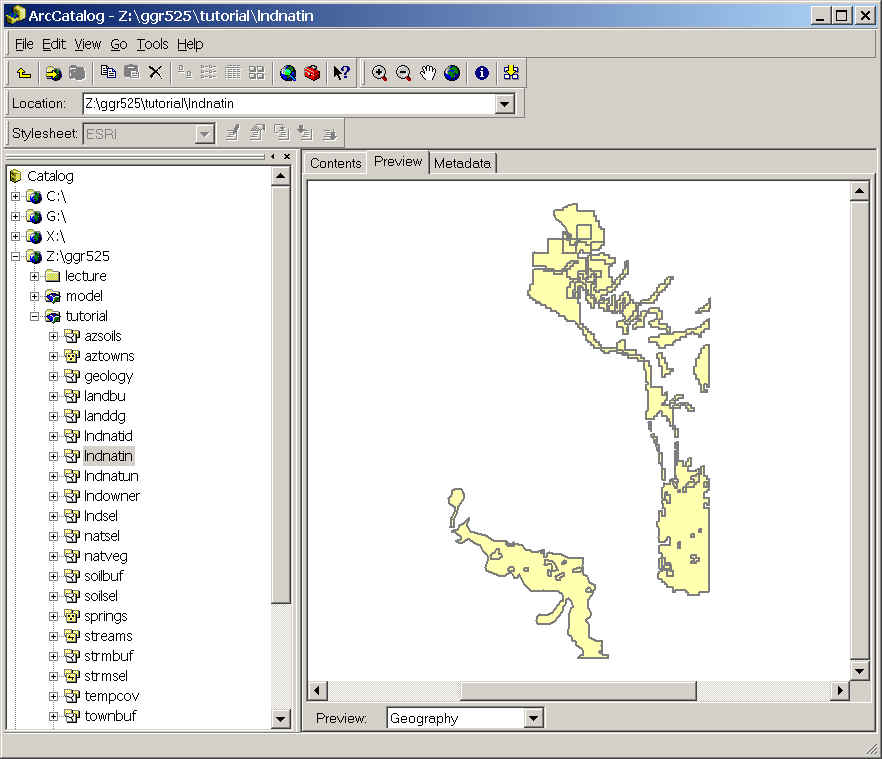
Step 9: You will not need these particular coverages again, so you can delete all coverages related to this exercise in ArcCatalog. You do not have to do this, but you will need disk space for your MODEL.
Step 10: Quit the programs and log off.